The brain is the most complex and vital organ of the human body, responsible for controlling all bodily functions, interpreting information from the outside world, and defining who we are as individuals. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the brain’s anatomy, functions, and common neurological conditions.
The brain is the most complex and vital organ of the human body, responsible for controlling all bodily functions, interpreting information from the outside world, and defining who we are as individuals. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the brain’s anatomy, functions, and common neurological conditions.
The human brain is a soft, spongy mass of tissue protected by the skull. It weighs approximately 1.3 to 1.4 kilograms in adults and is composed of billions of neurons and glial cells. The brain can be divided into three main parts: the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem.
Cerebrum
The largest part of the brain, responsible for higher brain functions such as thought, memory, emotions, and voluntary muscle movements.
Divided into two hemispheres (left and right) and four lobes:
Frontal Lobe: Associated with reasoning, planning, problem-solving, emotions, and motor functions.
Parietal Lobe: Processes sensory information related to touch, temperature, and pain.
Temporal Lobe: Involved in perception and recognition of auditory stimuli, memory, and speech.
Occipital Lobe: Responsible for visual processing.
Cerebellum
Located under the cerebrum, it is responsible for coordinating muscle movements, maintaining posture, and balance.
Brainstem
Connects the brain to the spinal cord and controls basic life functions such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure.
Comprised of three parts:
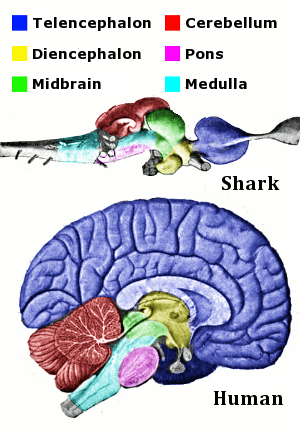
Midbrain: Involved in vision, hearing, and motor control.
Pons: Assists in regulating breathing and communication between different parts of the brain.
Medulla Oblongata: Controls autonomic functions like heartbeat and respiration.
Thalamus: Acts as a relay station, transmitting sensory and motor signals to the cerebral cortex.
Hypothalamus: Regulates homeostasis by controlling temperature, hunger, thirst, and hormonal processes.
Pituitary Gland: Often called the “master gland,” it controls other glands in the endocrine system.
Basal Ganglia: Involved in movement regulation and coordination.
Limbic System: Includes structures like the hippocampus and amygdala, essential for memory formation and emotional regulation.
The brain performs a wide array of functions necessary for survival and interaction with the environment. These can be broadly categorized as follows:
Sensory Processing
The brain receives and processes sensory input from the environment, including sight, sound, touch, taste, and smell.
Motor Control
It controls voluntary and involuntary muscle movements, enabling actions such as walking, talking, and breathing.
Cognitive Functions
These include thinking, memory, reasoning, problem-solving, and decision-making.
Emotional Regulation
The brain processes emotions and helps regulate mood and behavior.
Autonomic Functions
It manages involuntary functions such as heartbeat, respiration, digestion, and temperature regulation.
The brain requires a constant and rich supply of oxygenated blood, provided by four main arteries:
Carotid Arteries: Two large arteries on either side of the neck that supply most of the brain.
Vertebral Arteries: Two smaller arteries that join to form the basilar artery, supplying the back of the brain.
The blood vessels form a circular structure known as the Circle of Willis, ensuring continuous blood flow even if one artery is blocked.
Several conditions can affect the brain’s structure and function, leading to neurological disorders:
Stroke: Occurs when blood supply to part of the brain is interrupted, leading to tissue damage.
Alzheimer’s Disease: A progressive neurodegenerative disorder that causes memory loss and cognitive decline.
Parkinson’s Disease: A disorder of the central nervous system affecting movement and coordination.
Epilepsy: A neurological disorder characterized by recurrent seizures.
Multiple Sclerosis (MS): An autoimmune disease that damages the protective covering of nerves.
Brain Tumors: Abnormal growths of cells in the brain that can be benign or malignant.
Maintaining brain health is crucial for overall well-being. Here are some tips to promote a healthy brain:
Balanced Diet: Consume foods rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals.
Regular Exercise: Physical activity increases blood flow to the brain and promotes the growth of new neurons.
Mental Stimulation: Engage in activities that challenge your brain, such as puzzles, reading, and learning new skills.
Adequate Sleep: Sleep is essential for memory consolidation and overall brain function.
Stress Management: Chronic stress can negatively impact brain health.
Avoid Substance Abuse: Alcohol and drugs can damage brain cells and impair cognitive function.
The human brain contains approximately 86 billion neurons.
The brain generates about 20 watts of power while awake.
It uses around 20% of the body’s total energy.
The brain can process information as fast as 120 meters per second.
No two brains are exactly alike, making each individual unique.
India is home to some of the most skilled neurologists who specialize in treating various brain-related disorders. Here are a few renowned neurologists:
Dr. A.K. Banerji
Known as the father of neurosurgery in India, he has contributed significantly to the development of advanced neurosurgical techniques.
Dr. V.S. Mehta
A leading neurosurgeon with expertise in brain tumor surgery and spine surgery.
Dr. Sudhir Dubey
Specializes in minimally invasive brain and spine surgery.
Dr. B.K. Misra
Known for performing complex brain surgeries, including aneurysm and skull base surgeries.
Dr. Nand Kumar Yadav
An expert in treating epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, and movement disorders.
Several hospitals in India are renowned for their excellence in neurology and neurosurgery. Here are some of the best brain hospitals:
All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), Delhi
AIIMS is a premier medical institution offering comprehensive neurological care and research.
NIMHANS, Bangalore
National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences is a top center for neurological treatment and mental health care.
Apollo Hospitals, Chennai
Apollo Hospitals has a dedicated neuroscience department offering advanced treatments for brain disorders.
Fortis Hospital, Bangalore
Known for its state-of-the-art neurology and neurosurgery facilities.
Manipal Hospitals, Bangalore
Provides world-class treatment for neurological disorders and has a team of experienced neurosurgeons.
Medanta - The Medicity, Gurgaon
Offers cutting-edge technology and treatment options for brain and spine disorders.
Max Super Speciality Hospital, Delhi
Renowned for its advanced neurological care and minimally invasive surgeries.
Christian Medical College (CMC), Vellore
CMC is known for its high-quality neurological care and research.
Kokilaben Dhirubhai Ambani Hospital, Mumbai
Equipped with advanced diagnostic and treatment facilities for neurological disorders.
PGIMER, Chandigarh
Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research is a leading center for neurology and neurosurgery.
The human brain contains approximately 86 billion neurons.
The cerebellum coordinates voluntary movements, posture, and balance.
A stroke occurs when blood supply to part of the brain is interrupted or reduced, preventing brain tissue from getting oxygen and nutrients.
Engage in regular mental exercises, maintain a healthy lifestyle, get enough sleep, and manage stress.
A brain aneurysm is a bulge or ballooning in a blood vessel in the brain that can potentially rupture and cause a hemorrhagic stroke.
Treatment depends on the type, location, and stage of the tumor. Options include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy.
The brain communicates with the body through the spinal cord and a network of nerves that transmit signals to and from different body parts.